Install Postgres Locally
- Go to the download page
- Find the download for your operating system in the list.

- Download and run the package provided by the link.
- Follow prompts, make sure to write down the password you create for postgres user.
- Note the folder into which you install the application.
- Once installation has finished go to the folder you installed the application to and open PSQL.
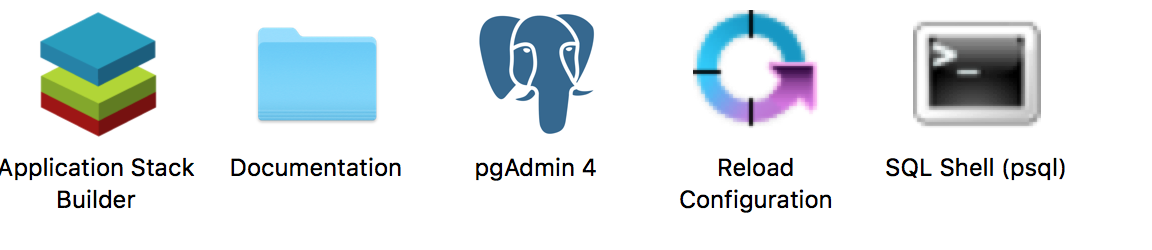
- You should see a series of prompts in the console. Assuming you selected the defaults when you were installing, you should just be able to hit enter to accept the defaults (i.e. [localhost] the default value is localhost).
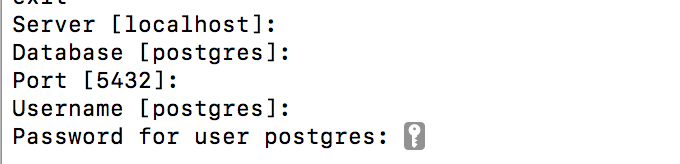
- Input the password you created in the step above.
- Now you should see the following prompt.
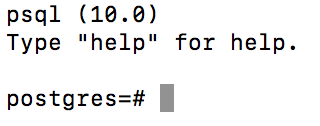
- Although Postgres is setup and working, we have not mapped some necessary properties to access the application through the command line. We will use this for functionality such as importing SQL scripts in later labs.
- Instruction for OSX
- Open a terminal
- Edit your
.bash_profilefile withvi ~/.bash_profile - Type
shift+gto get to the bottom - Type
oto start a new cursor on the last line - Type
ithis should provide you with a cursor to type - Type
export PATH=$PATH:/Library/PostgreSQL/10/bin - Hit
escthen:wqthis should close you out of vi - Close and reopen terminal
- Make sure it worked by typing in
psqlit should now be able to find the command.
- Windows
- Open the Windows menu
- Right click on My Computer and select properties
- Choose environmental variables
- Under the user section
3.If there is a PATH variable select that one for editing. Append the following
c:\Program Files\PostGres\bin- If there isn’t an existing PATH variable add a new one and input the following
%PATH%;c:\Program Files\PostGres\bin
- If there isn’t an existing PATH variable add a new one and input the following
- Open a command prompt
- type
psqland make sure that the application has been configured properly.
- Instruction for OSX
- Now you are ready to create your database from this class type
create database class;. This creates a table in the database called class. The semicolon is EXTREMELY important, otherwise it may be waiting for more commands and not actually creating the entry. - Now you should be able to type
\listand see your new database named class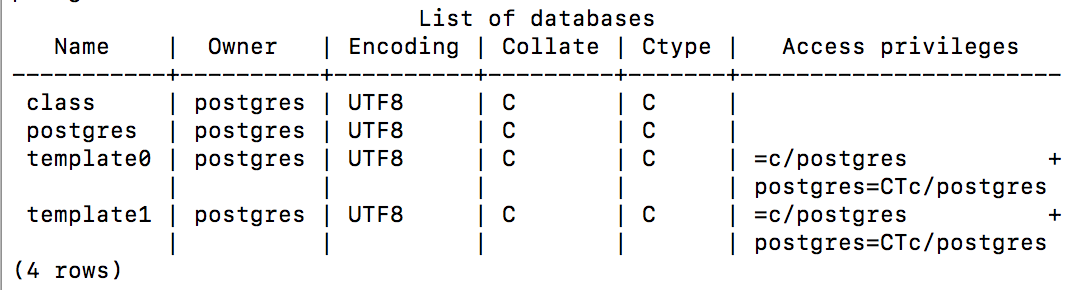
-
Now try connecting to the DB by issuing the following command
\c class. You should see the following…You are now connected to database "postgres" as user "jgleason". - Now let’s quit by issuing the
\qcommand
Review
In this lab we installed the PostGres DBMS and we created a new database and table. You should walk away from this lab understanding how to install and configure the Postgres DBMS.
Takehome Work
- Try to figure out how to configure the server. To accomplish this change the port from the default port used and connect using the new port.